Interstellar travel, the idea of exploring beyond our solar system to examine distant star systems has captivated human imagination for decades. Popularized by science fiction and fueled by scientific advancements, it raises profound questions about the future of humanity and our place in the universe. But is interstellar travel achievable, or is it a distant dream? Let’s hunt through the science, challenges, and possibilities of traveling to the stars.
What Is Interstellar Travel?
Interstellar travel refers to the ability to move between stars within a galaxy. Unlike space exploration confined to our solar system (e.g., trips to Mars or the Moon), interstellar travel aims to cross light-years to visit exoplanets orbiting distant stars. For instance, Proxima Centauri, the closest star system to Earth, is over 4 light-years away—equivalent to about 25 trillion miles.

Why Does Interstellar Travel Matter?
- Survival of Humanity: Earth faces challenges like climate change, natural disasters, and resource depletion. Colonizing other planets could ensure the long-term survival of our species.
- Scientific Discovery: Traveling to other star systems could provide answers about the origins of the universe, life on other planets, and the laws of physics.
- Human Curiosity: The innate desire to explore and push boundaries has driven every significant leap in human history, from crossing oceans to landing on the Moon.
The Science and Technology of Interstellar Travel
Interstellar travel faces monumental obstacles due to the vast distances involved, but ongoing scientific research offers potential solutions.
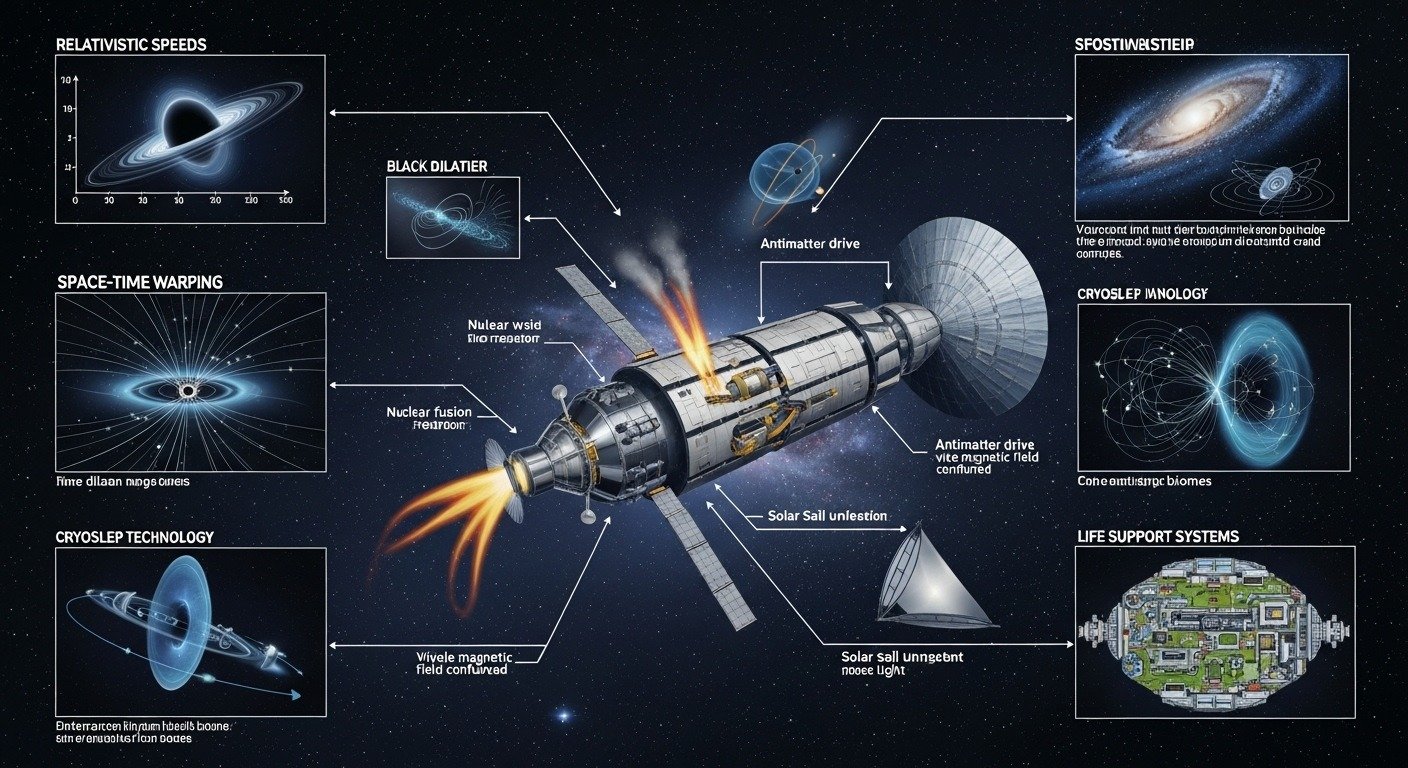
1. Current Propulsion Systems
Today’s spacecraft, like the Voyager probes, rely on chemical propulsion and gravitational assists. While revolutionary in the 20th century, these methods are far too slow for interstellar distances. At their current speed, it would take over 70,000 years to reach Proxima Centauri.
2. Advanced Propulsion Concepts
Scientists are exploring revolutionary propulsion technologies:
- Antimatter Engines: Antimatter annihilation releases massive amounts of energy, making it a promising but currently impractical option due to production and storage challenges.
- Light Sails: These harness the power of lasers or sunlight to propel a spacecraft at high speeds. Breakthrough Starshot, a project aiming to send tiny probes to Proxima Centauri, relies on this technology.
- Nuclear Propulsion: Utilizing nuclear reactions, such as fission or fusion, could offer higher energy outputs than chemical rockets.

Image Source: [Hackaday]
Challenges of Interstellar Travel
- Energy Requirements
The energy needed for interstellar journeys is astronomical. For example, achieving speeds close to light would require energy surpassing current global production capabilities. - Time and Human Longevity
Even at a fraction of light speed, trips to nearby stars could take decades or centuries. This raises questions about the feasibility of human crews and generational ships. - Radiation Exposure
Space travelers would be exposed to high levels of cosmic radiation, posing severe health risks. Shielding or genetic modifications might be necessary. - Communication Delays
Interstellar distances create significant communication delays. A signal to Proxima Centauri, for instance, would take over 4 years to arrive.
Potential Solutions and Theoretical Advances
1. Warp Drives
Popularized by science fiction, warp drives theoretically allow for faster-than-light travel by bending space-time. While highly speculative, concepts like the Alcubierre Drive are under theoretical investigation.
2. Cryogenic Sleep
Suspending human metabolism through cryogenic technology could enable long-duration voyages, though this technology remains experimental.
3. AI and Robotics
Unmanned probes equipped with artificial intelligence could precede human missions, exploring and preparing distant worlds for human arrival.

Image Source: [JSTOR Daily]
Ethical and Philosophical Considerations
- Should We Go?: Critics argue that we should focus on solving Earth’s problems before venturing to other worlds.
- Impact on Alien Ecosystems: If we find life, colonization could disrupt native ecosystems and cultures, as seen in Earth’s history.
What Lies Ahead?
While interstellar travel remains in the realm of possibility rather than reality, every small step brings us closer. Projects like Breakthrough Starshot and NASA’s interstellar probe designs are paving the way for future exploration. Advances in propulsion, AI, and space habitation could make interstellar travel achievable within the next few centuries.

Conclusion
Interstellar travel is a monumental challenge, but it also represents humanity’s greatest dream. By pushing the boundaries of science and technology, we not only move closer to the stars but also deepen our understanding of ourselves and our place in the cosmos. While it may not happen tomorrow, the pursuit of interstellar travel ensures that humanity continues to innovate, explore, and hope.






0 Responses