Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are buzzwords dominating the tech industry. But while these terms are often used interchangeably, they are not the same. AI is the broad concept of machines mimicking human intelligence, while Machine learning is a subset of AI focused on learning from data. This blog explores their differences, applications, and impact on our world.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence refers to machines or systems designed to simulate human intelligence. AI enables computers to perform tasks such as:
- Understanding language
- Recognizing speech and images
- Problem-solving and decision-making
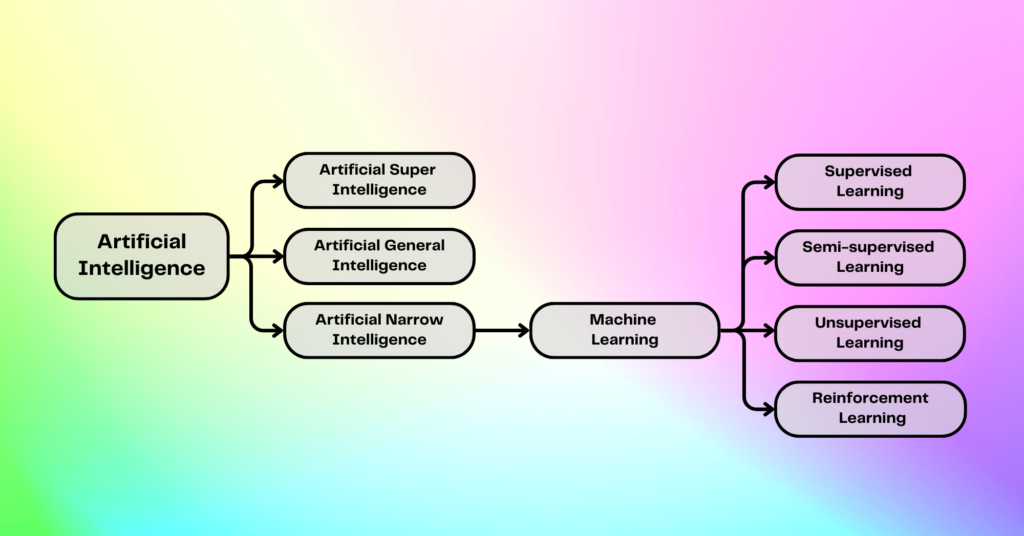
AI can be broadly categorized into two types:
- Narrow AI: Designed for specific tasks (e.g., Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant).
- General AI: Theoretical machines capable of human-level intelligence across any field (still under development).

What Is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that enables machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Instead of following static rules, ML algorithms analyze patterns in data to make decisions.
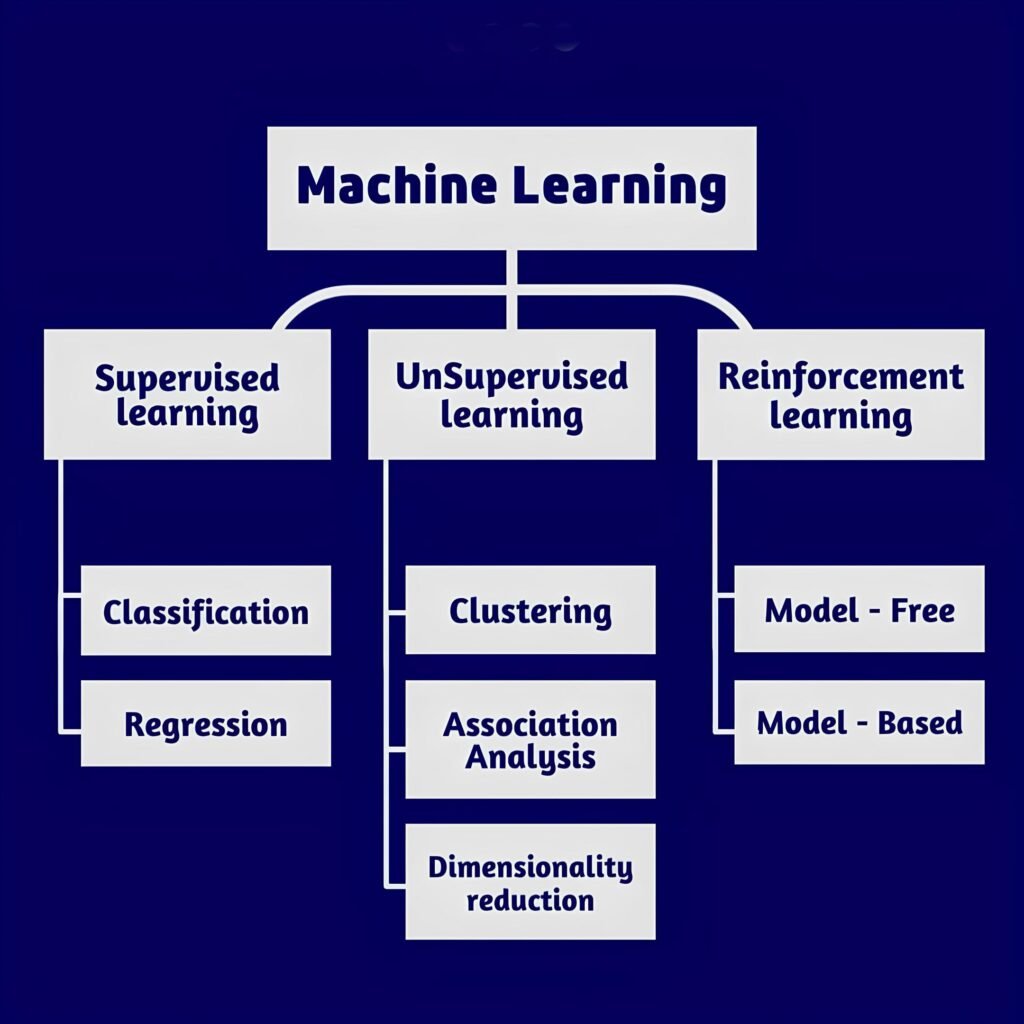
There are three main types of Machine Learning:
- Supervised Learning: Trains on labeled data (e.g., spam email detection).
- Unsupervised Learning: Works with unlabeled data to find patterns (e.g., customer segmentation).
- Reinforcement Learning: Learns through rewards and penalties (e.g., game-playing AI).
Key Differences Between AI and Machine Learning
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence | Machine Learning |
| Definition | Simulates human intelligence | Focuses on learning from data |
| Goal | Mimic human behavior and decision-making | Improve performance through data and experience |
| Scope | Broad and includes various techniques like ML, NLP | A subset of Artificial Intelligence |
| Examples | Chatbots, Self-Driving Cars, Robotics | Netflix Recommendations, Spam Filters |
| Input | Algorithms and pre-set rules | Data and statistical models |
Real-World Applications of AI and Machine Learning
Applications of Artificial Intelligence:
- Healthcare: AI diagnoses diseases using medical imaging.
- Finance: AI automates fraud detection and risk analysis.
- Retail: AI-driven chatbots assist customers.
Applications of Machine Learning:
- Entertainment: Netflix and Spotify recommend shows and songs.
- E-Commerce: Amazon predicts user preferences for product recommendations.
- Marketing: ML analyzes customer data for targeted campaigns.

Image Source: [DataCamp]
How AI and Machine Learning Work Together
Machine Learning is often the driving force behind AI applications. For example:
- AI-powered Voice Assistants (like Siri): Use ML to understand and respond accurately.
- Self-Driving Cars: Combine AI for decision-making and ML for real-time data learning.
Both technologies complement each other to automate and optimize processes.
Future of AI and Machine Learning
The future of AI and ML is promising, with advancements in areas like:
- Healthcare: AI predicting diseases earlier through smarter algorithms.
- Automation: Businesses using AI-driven automation for efficiency.
- Sustainability: ML algorithms optimizing energy consumption and waste management..
However, challenges remain, including ethical concerns, job displacement, and data privacy issues.
Conclusion
While AI and ML are closely connected, they serve different purposes. AI aims to mimic human intelligence broadly, while ML focuses on learning from data to make machines smarter. Both technologies are revolutionizing industries and changing how we live and work.
Understanding the difference between AI and ML will help businesses and individuals harness their power effectively. Visit Website







0 Responses